H.265 is also known as HEVC, which stands for High Efficiency Video Coding
H.265 is a new compression specification that is making its way into the industry as the successor of H.264. This makes it a candidate for a future video codec in WebRTC.
Like H.264, H.265 is royalty bearing and is governed by the MPEG-LA, although exact patent holders and costs are yet to be organized.
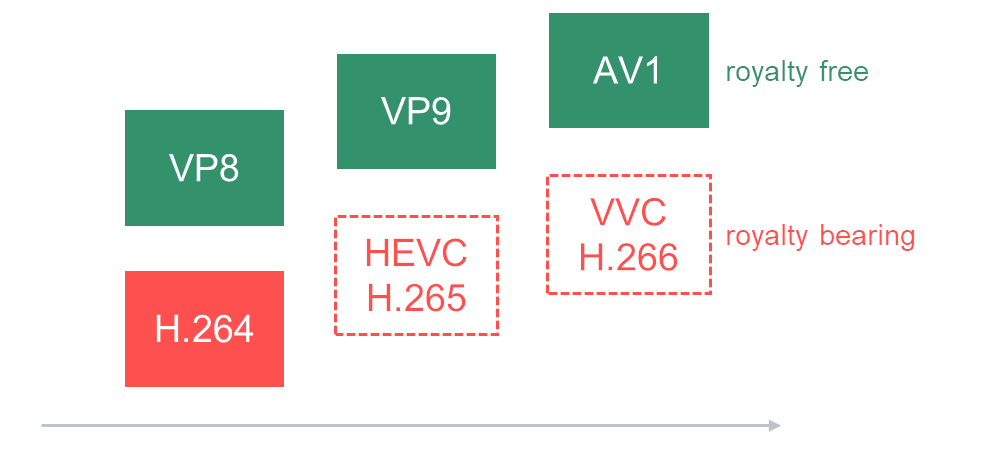
H.265 is assumed to be more CPU intensive than H.264 with better compression results. Its main “competitor” in WebRTC is VP9.
Technical Advancements
From a technical standpoint, H.265 offers significant improvements over H.264. It utilizes advanced algorithms and coding techniques to achieve up to 50% bitrate reduction while maintaining the same video quality. This is achieved through features like Coding Tree Units (CTUs), which allow for more flexible partitioning of the video frame, and improved motion compensation algorithms. The codec also supports resolutions up to 8K, making it future-proof for emerging high-definition formats.
WebRTC and H.265
In the context of WebRTC, adopting H.265 means focusing on Apple devices (Mac, iPhone and iPad via Safari browsers). It is worth noting that H.265 is not yet universally supported in WebRTC implementations due to licensing complexities and hardware constraints.
Licensing and Adoption
One of the major hurdles for the widespread adoption of H.265 is the licensing model. Unlike its predecessor, H.265 has multiple patent pools, making it more expensive to implement. This has led to slower adoption rates, especially among open-source projects and smaller enterprises.
Additional reading
- WebRTC video codec generations: Moving from VP8 and H.264 to VP9 and AV1
- What are the Implications of VP9 (or H.265) on WebRTC?
- Thoughts on Apple, WebRTC, HTML5, H.265 and VP9
- AV1 vs HEVC: Are the WebRTC codec wars back?
- Which video codec to use in your WebRTC application?
- WebRTC & HEVC – how can you get these two to work together


