M2M is built up of 3 main components: data producers, data aggregators and controllers
M2M fascinates me. If I had to guess why it probably has to do with the communication and network nature of it – it is at the same time similar and different than VoIP.
With Google just acquiring Nest, I just had to write my own piece about M2M – something I wanted to do for a while anyway.
Before I start with my own ramblings about how I see the M2M networks, I’d like to share two great posts I’ve read this week about it, and a book I really enjoyed:
- Dr Richard Windsor about the Nest acquisition, with a simple statement: “The world is not becoming less siloed but more.”
- Robert X. Cringely predicting the Internet of Crap – why vulnerabilities will make us throw away and replace all of our current networking equipment and devices
- Rainbows End by Vernor Vinge. Go read it now. I’ll wait. It has everything and anything you need to know about where we’re headed with M2M
–
Machine to Machine (M2M). Internet of Things (IoT). Internet of Everything (IoE). They are all one and the same. Probably coined by different vendors just to show they are thought leaders in this domain. They throw number into the air – everything between 10 billion to a trillion devices. Pick a number and a year, and you have yourself a prediction.
When this brave new world arrives, what will connect all of these devices? How will the network architecture look like?
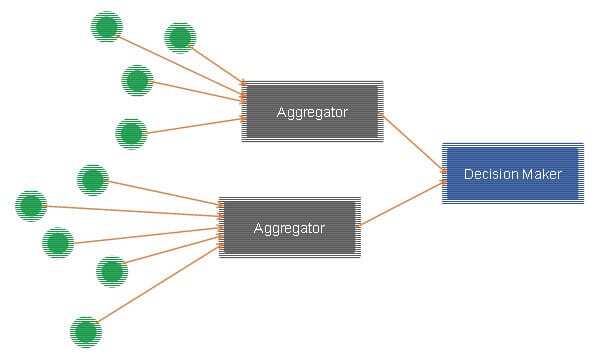
Here’s what I think: There are 3 types of jobs that need to be done: you either produce data, aggregate and process data or make decisions. And you can do more than a single task.
- Producing data – this is the work done by sensors. They can be connected wirelessly or by other means to “something” that collects that information and is capable of sending it elsewhere. I think this is what we’re seeing today: be in Nest, or these new wristbands that are popping everywhere.
We have our hacker’s platforms for these toys: Arduino and Raspberry Pi. Consider them first generation and wait to see them shrink and improve.
- Aggregators – these are the machines than and up gobbling data from sensors and processing it. They can filter information, aggregate it, and make calculations on top of it. It is where Big Data and analytics will find a cozy home – a place where ridiculously huge amounts of data need to be collected.
- Decision makers – all that data is collected for a reason, and that reason may be to show a fancy visual on a dashboard in your smartphone; or to drive a decision – lower the temperature on that Nest thermostat as an example.
This model is different than the one of VoIP, where everyone is both a client and a server. It is also different than the one of the web, where you are either a client (web browser) or a server. It seems to me like a hybrid of sorts between the two – which is exactly where you’ll find something like WebRTC.
But more on that – in a later post.

Nice post. There is definitely a link between WebRTC and the Internet of Things. I’ve recently shifted my development efforts from Twelephone (http://twelephone.com) to Skynet (http://skynet.im), an open source machine-to-machine instant messaging platform.
My new plan is to rewrite Twelephone to run on top of Skynet so that it handles all of the signaling and messaging between users. There’s no reason why people can’t have UUIDs like the machines connected to Skynet and perhaps communicate with them too on the same network. Industry experts are starting the call this idea the Internet of Everything.
Now I just need to figure out how to leverage the WebRTC data channel for M2M communications 😉
It seems to me that there is an architectural difference between making a decision and enacting the decision. Getting the decision back into the real world to perform an action may be via the same devices that produce the data in the first place (like Nest) but not necessarily.
What do you think?
Oh, and thanks for the recommendation on Rainbows End. I enjoyed his earlier books and am currently enjoying this one 🙂
Rik,
I think each of the 3 “components” I mentioned can be packed into a specific device. You can have all 3 bunched together, you can have the decision making alone happen on a smartphone or in the cloud, you can have aggregation done closer to the devices.
And yes, you are correct – making a decision and enacting upon it can and should be separated.
As for Rainbows End – I am glad you like it.